
How to use
ADTransitionController brings all the power of the Core Animation framework to your apps with nice pre-defined transitions.
- For apps supporting iOS 7 and beyond, we have a very generic API that uses the new
UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegateprotocol, making it usable for any transition (navigation, modal, tab bar). - If you also need to support iOS 6, we give you a drop-in replacement for UINavigationController that adds support for our transitions.
Installation
Basic
- Add the content of the
ADTransitionControllerfolder to your iOS project - Link against the
QuartzCoreFramework if you don't already - Import
ADTransitionController.hin your project
CocoaPods
- Add
pod 'ADTransitionController'to yourPodfile - In your terminal run
$ pod installand open your workspace$ open yourApp.xcworkspace - Import
<ADTransitionController.h>in your project
ARC
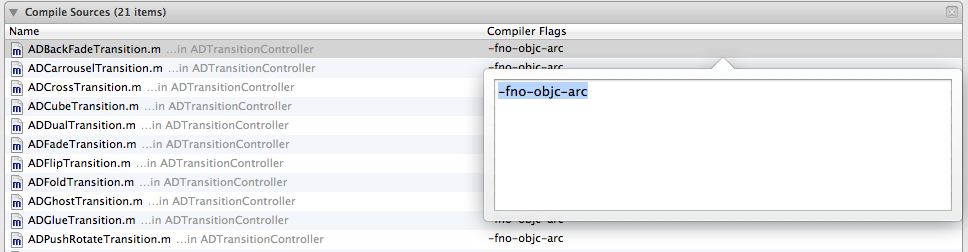
If you are working on an ARC project, use the -fno-objc-arc flag in Build Phases > Compile Sources.
Example
Your project is now ready to take advantage of ADTransitionController. Here are two examples of how to use it. One if you plan to develop for iOS 7 and later, the other one if you want to support iOS 6 too.
iOS 7 and later
We're making use of the new UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate protocol. The API provided by Apple is quite complex, but we made it very simple to use.
In short:
- Set the delegate of your navigation controller to the one that we give you.
- Make your view controller inherit from
ADTransitioningViewController(if this is not an option for you, see below). - Set the
transitionproperty of your view controller to your favorite transition.
In details:
First of all, create your UINavigationController and set its delegate to a ADNavigationControllerDelegate instance.
#import "ADNavigationControllerDelegate.h"
...
UINavigationController * navigationController = [[UINavigationController alloc] initWithRootViewController:viewController];
ADNavigationControllerDelegate * navigationDelegate = [[ADNavigationControllerDelegate alloc] init];
navigationController.delegate = navigationDelegate;
self.window.rootViewController = navigationController;
[navigationController release];
...
[navigationDelegate release];
Then create your new controller (that inherits from ADTransitioningViewController), set its transition and push it onto the stack. In this example, this will animate the transition with a cube effect.
UIViewController * newViewController = [[UIViewController alloc] init];
ADTransition * transition = [[ADCubeTransition alloc] initWithDuration:0.25f orientation:ADTransitionRightToLeft sourceRect:self.view.frame];
newViewController.transition = transition;
[self.navigationController pushViewController:newViewController animated:YES];
[transition release];
[newViewController release];
If your view controller can't inherit from ADTransitioningViewController, you can use directly an ADTransitioningDelegate object to control the transition.
UIViewController * newViewController = [[UIViewController alloc] init];
ADTransition * transition = [[ADCubeTransition alloc] initWithDuration:0.25f orientation:ADTransitionRightToLeft sourceRect:self.view.frame];
ADTransitioningDelegate * transitioningDelegate = [[ADTransitioningDelegate alloc] initWithTransition:transition];
newViewController.transitioningDelegate = transitioningDelegate;
[self.navigationController pushViewController:newViewController animated:YES];
[transition release];
[newViewController release];
...
[transitioningDelegate release];
Under the hood
To create a custom animation, Apple provides different protocols we have implemented for you : UIViewControllerTransitioningDelegate, UIViewControllerAnimatedTransitioning, UIViewControllerContextTransitioning. That way, you shouldn't bother to dig into these APIs.
As we have just seen it, in practice, what you only have to do on iOS7 is to create a UINavigationController, and a ADTransition.
To sum up, we provide three different classes you may want to use :
ADNavigationControllerDelegate: used when you setup your navigation controller to perform custom animationsADTransitioningViewController: used for your view controllers to control their transitionsADTransitioningDelegate: used only if you can't inherit fromADTransitioningViewControllerand need to specify the transitioning delegate for the view controller
iOS 6 and later
If you need to support earlier versions of iOS, this is possible. Just use ADTransitionController instead of UINavigationController.
Instantiate an ADTransitionController like a UINavigationController:
UIViewController * viewController = [[UIViewController alloc] init];
ADTransitionController * transitionController = [[ADTransitionController alloc] initWithRootViewController:viewController];
[viewController release];
self.window.rootViewController = transitionController;
[transitionController release];
To push a viewController on the stack, instantiate an ADTransition and use the pushViewController:withTransition: method.
- (IBAction)pushWithCube:(id)sender {
UIViewController * viewController = [[UIViewController alloc] init];
ADTransition * transition = [[ADCubeTransition alloc] initWithDuration:0.25f orientation:ADTransitionRightToLeft sourceRect:self.view.frame];
[self.transitionController pushViewController:viewController withTransition:transition];
[transition release];
[viewController release];
}
To pop a viewController from the stack, just use the popViewController method.
- (IBAction)pop:(id)sender {
[self.transitionController popViewController];
}
Note
When a UIViewController is pushed onto the stack of view controllers, the property transitionController becomes available to the controller (see example above: self.transitionController). This way, an ADTransitionController can be used like a UINavigationController.
ADTransition subclasses
For now, the built-in transitions available are the following. Try out our demo application to see them in action!
ADCarrouselTransition, ADCubeTransition, ADCrossTransition, ADFlipTransition, ADSwapTransition, ADFadeTransition, ADBackFadeTransition, ADGhostTransition, ADZoomTransition, ADSwipeTransition, ADSwipeFadeTransition, ADScaleTransition, ADGlueTransition, ADPushRotateTransition, ADFoldTransition, ADSlideTransition.
ADTransitionController API
The ADTransitionController API is fully inspired by the UINavigationController, to be very easy to integrate in your projects. The few differences between the two APIs are presented below.
Methods
The point of ADTransitionController is to be able to customize the animations for a transition between two UIViewController instances. Here are the methods we added to let you take advantage of the built-in transitions:
- (void)pushViewController:(UIViewController *)viewController withTransition:(ADTransition *)transition;
- (UIViewController *)popViewControllerWithTransition:(ADTransition *)transition;
- (NSArray *)popToViewController:(UIViewController *)viewController withTransition:(ADTransition *)transition;
- (NSArray *)popToRootViewControllerWithTransition:(ADTransition *)transition;
Here are the convention for the push and pop actions:
- pass
nilto the transition parameter to disable the animation. Thus the transition won't be animated. - pass an
ADTransitioninstance to the transition parameter to animate the push action. - by default the pop action uses the reverse animation used for the push action. However you can pass a different transition to the transition parameter to change this behavior.
Delegate
Like a UINavigationController, an ADTransitionController informs its delegate that a viewController is going to be presented or was presented. The delegate implements the ADTransitionControllerDelegate protocol.
@property (nonatomic, assign) id<ADTransitionControllerDelegate> delegate;
@protocol ADTransitionControllerDelegate <NSObject>
- (void)transitionController:(ADTransitionController *)transitionController willShowViewController:(UIViewController *)viewController animated:(BOOL)animated;
- (void)transitionController:(ADTransitionController *)transitionController didShowViewController:(UIViewController *)viewController animated:(BOOL)animated;
@end
Going Further
If you want to totally take control of the ADTransitionController API, feel free to create your own transitions and animations!
All you need to do is to subclass ADDualTransition or ADTransformTransition and implement a init method.
The simplest example of a custom transition is the ADFadeTransition class. The effect is simple: the inViewController fades in. For this the inViewController changes its opacity from 0 to 1 and the outViewController from 1 to 0.
@interface ADFadeTransition : ADDualTransition
@end
@implementation ADFadeTransition
- (id)initWithDuration:(CFTimeInterval)duration {
CABasicAnimation * inFadeAnimation = [CABasicAnimation animationWithKeyPath:@"opacity"];
inFadeAnimation.fromValue = @0.0f;
inFadeAnimation.toValue = @1.0f;
inFadeAnimation.duration = duration;
CABasicAnimation * outFadeAnimation = [CABasicAnimation animationWithKeyPath:@"opacity"];
outFadeAnimation.fromValue = @1.0f;
outFadeAnimation.toValue = @0.0f;
outFadeAnimation.duration = duration;
self = [super initWithInAnimation:inFadeAnimation andOutAnimation:outFadeAnimation];
return self;
}
@end
This example is really basic and if you want to create more funky effects, just have a look to the following API and the examples we provided.
ADTransition API
The ADTransition class is an abstract class that has two abstract subclasses: ADDualTransition and ADTransformTransition.
Instances of ADDualTransition have two importants properties:
@property (nonatomic, readonly) CAAnimation * inAnimation;
@property (nonatomic, readonly) CAAnimation * outAnimation;
The inAnimation is the CAAnimation that will be applied to the layer of the viewController that is going to be presented during the transition.
The outAnimation is the CAAnimation that will be applied to the layer of the viewController that is going to be dismissed during the transition.
Instance of ADTransformTransition have three importants properties:
@property (readonly) CAAnimation * animation;
@property (readonly) CATransform3D inLayerTransform;
@property (readonly) CATransform3D outLayerTransform;
The inLayerTransform is the CATransform3D that will be applied to the layer of the viewController that is going to be presented during the transition.
The outLayerTransform is the CATransform3D that will be applied to the layer of the viewController that is going to be dismissed during the transition.
The animation is the CAAnimation that will be applied to the content layer of the ADTransitionController (i.e. the parent layer of the two former viewController layers).
Future Work
There are a couple of improvements that could be done. Feel free to send us pull requests if you want to contribute!
- Add new custom transitions
- Add support for non plane transitions (Fold transition for instance)
- More?
Download
Start to use ADTransitionController and take advantage of the custom transitions.
License
Copyright (c) 2013, Applidium All rights reserved. Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
- Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
- Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
- Neither the name of Applidium nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE REGENTS AND CONTRIBUTORS ``AS IS'' AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE REGENTS AND CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.